We know about the viruses and their ability to destroy the device through their infection. One peculiarity of the viruses in the malware family is they have self-replicating properties. Today this article talks about the infamous ILOVEYOU virus that has caused havoc in cyberspace since its inception in 2000. The virus that originated in Manila has so far caused damage to around millions of devices that incurred loss of billion dollars.
Read more about the Love Bug virus and its mitigation strategies to safeguard your device from infection.
ILOVEYOU Virus- Know about a virus that can destroy your device
ILOVEYOU virus is one of those viruses that spread only through emails. As of now, over 50 million devices have been infected with total damage of approximately 7 billion USD.
History of the Love Bug Virus
The ILOVEYOU bug was invented in 2000 by a Manila-based resident called Onel De Guzman. The entire motivation behind creating malware was to steal users’ credentials and have access to the Internet, given the poor financial conditions of Onel.
The code that was supposed to run in the Philippines spread worldwide because Onel thought of removing the geographical restrictions. He quickly worked on the Windows vulnerability that enabled the execution of scripting languages sent over emails as attachments.
Over time, various anti-virus companies rolled out patches and immediate fixes to control the damage. But on the other hand, it encouraged different hackers to roll out the variants of the Love Bug virus and keep this infection going under various names.
Infection Process of the ILOVEYOU Virus
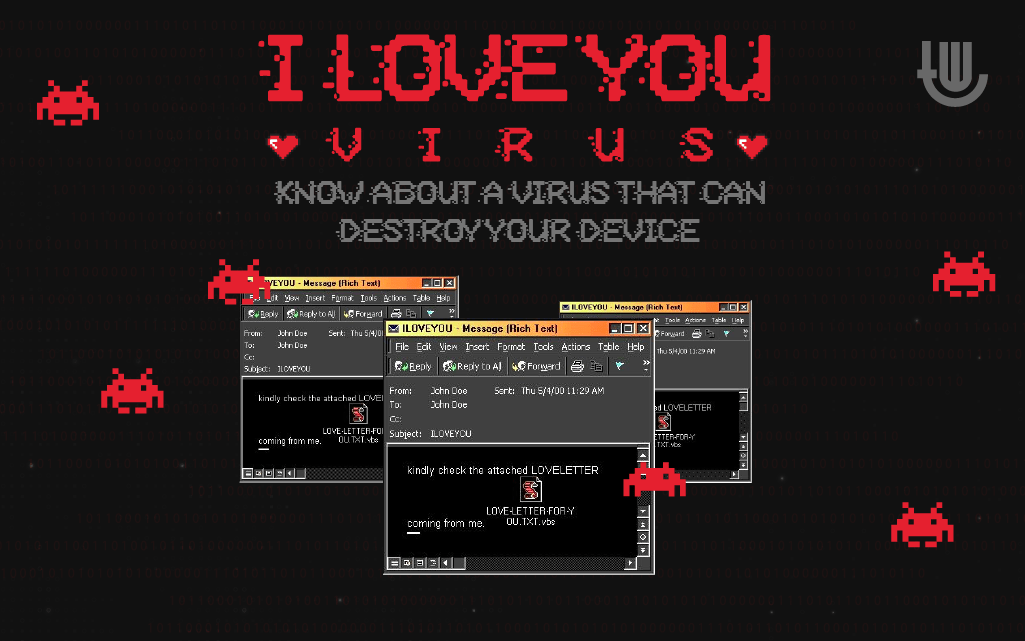
The infection process of the virus remains not so complicated as it spreads through email on Microsoft Outlook. The subject is ‘ILOVEYOU’ with an attachment titled, ‘LOVE-LETTER-FOR-YOU.TXT.vbs.’ The email also contained a body that stated, ‘kindly check the attached LOVELETTER coming from me.’
Once executed, the virus spreads to every contact on the mailing list and, at the same time, self-replicates itself on the victim’s device by making malicious copies of existing files. This leads to the propagation of the virus to other devices and destroys the infected device’s functioning alongside.
The malware often downloads a backdoor or a trojan that enables the hacker to have continued access to a device. Barok trojan was utilized in this case, which doesn’t propagate or spread by itself but provides unauthorized access.
The victim’s device would have various files, such as sensitive documents to media formats, renamed and deleted from the system. Also, the virus constantly scraped for any credentials and shared them over the server to the attacker.
As the virus spread across various regions, it infected different industry sectors such as banking, telecoms, government entities, automobiles, etc.
Mitigation Steps
One of the most robust means to evade infection from worms or viruses is to have a strong anti-virus that frequently checks for the files over the network and scans them. A strong anti-virus program can quarantine the infected files before any severe damage occurs.
Besides that, humans are found to be the weakest link for a cyber incident to take place. The smallest of mistakes can have devastating outcomes. Following are the steps that one can take as a precaution from infection:
- Avoid clicking on any links or attachments that are received from unknown sources.
- Lookout for certain anomalies in the emails, such as unusual extensions or double extensions.
- One can always screen such files through strong virus checkers and quarantine them.
- All the precautionary steps need to be followed even when there are emails from known sources since they might not be direct propagators of malware but might unknowingly pass it.
If you are someone who has been infected with the ILOVEYOU virus, it is essential to isolate the infected device from the network. Reboot the computer in safe mode to handle the virus and look for any effective patches that can remediate this issue.
Various password-stealing malware are actively being re-developed for better stealing functionality and improved stealthiness. Notable names are Redline, Agent Tesla, Ficker, Meta, Zingostealer, etc.
Towards the conclusion
This article provided comprehensive information on the Love Bug or ILOVEYOU virus. True, even today, there might be numerous unknown vulnerabilities that the hackers might exploit for their selfish reasons. However, it is crucial to start taking security seriously and personally as soon as possible.
Keeping an eye on the latest security trends, patches, and incidents can bring about a massive change in how we see security. It gives us an insight into how attacks are executed and what is being done to protect from them. However, today the bug might not get as much attention as it did for the ILOVEYOU virus in 2000.
Modern-day stealers are stealthy and often go undetected. We hope you stay safe and protected from cyberspace while surfing the Internet.

Author Bio: This article has been written by Rishika Desai, B.Tech Computer Engineering graduate with 9.57 CGPA from Vishwakarma Institute of Information Technology (VIIT), Pune. Currently works as Threat Intelligence Researcher in CloudSEK. She is a good dancer, poet and a writer. Animal love engulfs her heart and content writing comprises her present. You can follow Rishika on Twitter at @ich_rish99.