The Windows Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a network communication protocol that enables remote communication between two devices. It is Microsoft’s proprietary protocol to provide network access over an encrypted channel for remote users. RDP is commonly used by network administrators to diagnose problems, log in to servers, and carry out other actions.

How RDP works:
The Remote Desktop Protocol requires two components for successful remote connection. These are:
- RDP server
- RDP client
Your Windows PC serves as a typical RDP server, while any computer with an RDP client app installed acts as an RDP client. Microsoft features its own client app for Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android, with alternatives available for Linux OS and other platforms.
RDP is responsible for transmitting screen information from the remote server to the RDP client. It also shares input from the client’s peripheral devices like keyboard and mouse with the RDP remote server. However, most of the data flow from the RDP server to the client as the graphical screen information is extensive compared to data from the peripheral devices.
RDP requires additional protocols for successful remote connection. These include the TPKT that enables translation of information units between the two suites of networking protocols called TCP and ISO so its a good thing if your company needs remote desktop services. RDP also needs X.224 and T.125 MCS to set up a remote connection and enable multiple channels.
RDP Port:
Port 3389 is the default port to power Remote Desktop Services on Windows operating system. The Remote Desktop feature must be enabled on a PC before it can listen to remote connections on port 3389. Since this port is well known to script kiddies and bots, it is often an easy target for exploitation. Therefore, proper security measures need to be taken to avoid cyberattacks.
Security vulnerabilities:
The Multi-State Information Sharing and Analysis Center (MS-ISAC) observed a 153 percent increase in cyber-attacks in 2019. Many of these attacks led to significant network downtime and resulted in costly remediation efforts. The MS-ISAC attributes the surge to ransomware infections affecting Managed Service Providers.

Ransomware attacks are malware attacks that block access to systems and their resources until the ransom is paid. Ransomware attackers encrypt critical files on the infected system, block their access, and threaten to delete them if the victims refuse to submit to their demands. These demands, often in the form of ransom amounts, are typically displayed as a ransom note on the victim’s screen.
As a result of security compromises and vulnerabilities, victims lose access to important systems and files and experience significant financial losses due to legal costs and restitution efforts. The effects of these attacks can be particularly catastrophic when emergency services like 911 call centers and critical infrastructure like hospitals fall victim to it.
To prevent your network from such attacks, network administrators and engineers recommend changing the default RDP port as the first line of defense. While this may not fool a smart attacker, it certainly limits the number of attacks.
How to modify the RDP Port?
Changing the default RDP port from 3389 requires editing in the Windows registry. Changing the registry may be risky; therefore, it is a good idea to back up your data before saving any changes.
Here is how you can modify the RDP port by editing the registry value.
- Type regedit in the Command Prompt to enter the Registry Editor.
- Locate the following registry branch/subkey and click it.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp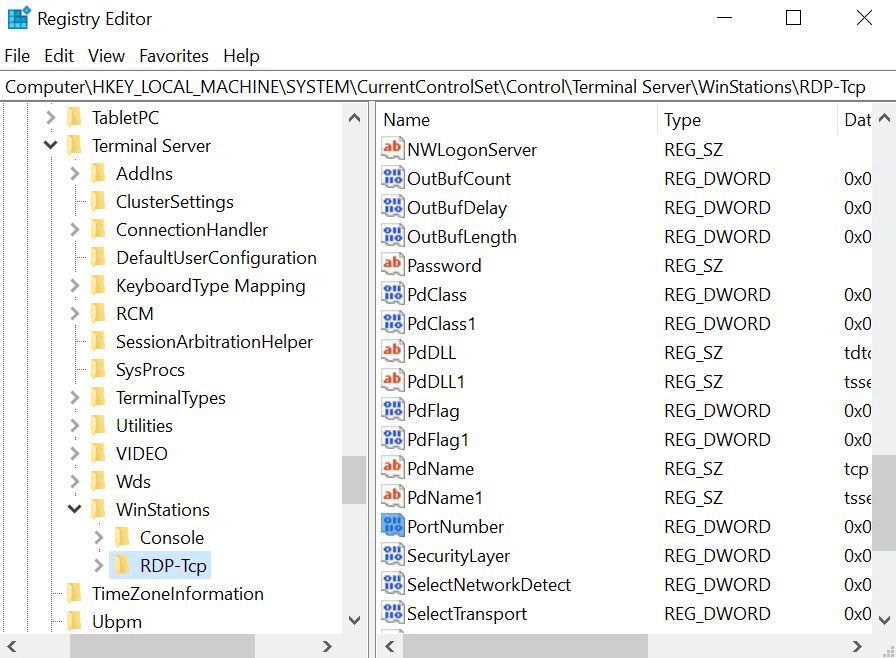
- Navigate to the registry entry PortNumber in the Edit menu.
- Click on Modify and select Decimal in the “Edit DWORD Value” window.
- Type a new port number and select OK when done.
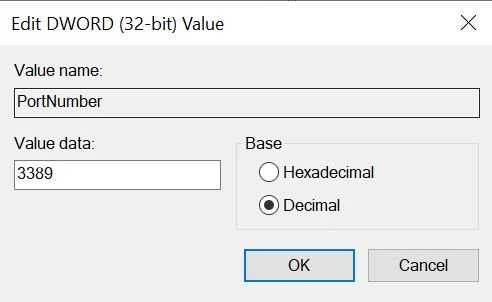
Reboot the system for the new port assignment to take effect. The system should now specify the new port in the client properties.
If you do not use port 3389 as a default RDP port, you can look up the current RDP port number by using the following command:
Get-ItemProperty -Path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP Tcp' -name "PortNumber"Additional recommendations:
To further protect your network and resources, there are more steps that you can take to safeguard your devices and avoid losses and severe downtime.
- Set up strong passwords and enable multi-factor authentication.
- Place good account lockout policies. Lack of account lockout policy means that the RDP protocol can be used to access the admin password with brute force attacks. In brute force attacks, the hacker tries all possible passwords to login into the network.
- Allow remote access to RDP clients you trust.
- Follow the Principle of Least Privilege, which limits the level of access required to perform duties.
- Make sure that only authorized users can access the network. Review RDP login attempts from anonymous hosts and look for any anomalous activity on the network.
- Regularly update the RDP server and client software to ensure that the latest versions are installed on your system.
Final thoughts:
With the Windows Remote Desktop feature, you can connect two devices with the right RDP server and client apps installed on them. Once connected, you can view content on the remote display, access files, and interact with the local device using RDP. However, with the exponential rise in the number of cyberattacks, you must take security measures to protect your data from prying eyes.

Author Bio: Audrey Throne has an ongoing affair with the words that capture readers’ attention. Her passion for writing dates back to her pre-blogging days. She loves to share her thoughts related to business, technology, health and fashion.
Find her on Twitter: @audrey_throne