X-rays are electromagnetic waves whose wavelengths are 1000 times shorter compared to light rays. Discovered in 1895 by physicist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, X-rays have since played a critical role in modern technology across different industries. While working in his lab, Röntgen accidentally discovered these rays, which he called x-rays due to their unknown nature.
Having deeply studied these rays, Röntgen discovered that they could penetrate human flesh and be photographed. However, he found out that these rays couldn’t penetrate high-density objects such as bones and lead.
The discovery was hailed and soon became an essential diagnostic tool in medicine, allowing doctors to, for the first time, see the inside of the human body without conducting surgery on it. This technology was later applied in the military field where, during the Balkan war, it was used to find bullets and broken bones in the patient’s body.
Even with these discoveries, little was known about the harmful nature of the X-rays. The technology was used without understanding how it was negatively impacting the users. This was the case until Clarence Dally, who was deeply involved in the use of X-Rays died of skin cancer. This death led scientists to start taking these rays seriously.
By the 1950s, the everyday use of these x-rays was stopped due to the risks they posed to the users. With due care, this technology has been adopted in different fields such as medicine, security, material analysis, military, and many more.
The Role of X-rays in Security Inspections
With the increased insecurity cases across the globe, there’s greater demand for a secure yet accurate system of inspecting material and checking people to guarantee secure environments. With this demand, the x-ray security inspection system provides the much needed non-contact visual inspection of people as well as detecting dangerous or smuggled material.
A full-body screening and inspection system innovatively combined with artificial intelligence is capable of providing excellent automated processing, throughput rates, and threat recognition in seconds. This way, people, ships, airports, national boundaries, mass ventures, and critical infrastructure are safeguarded against modern threats that include terrorism and drug and human trafficking.
X-Ray Used in Baggage Checking
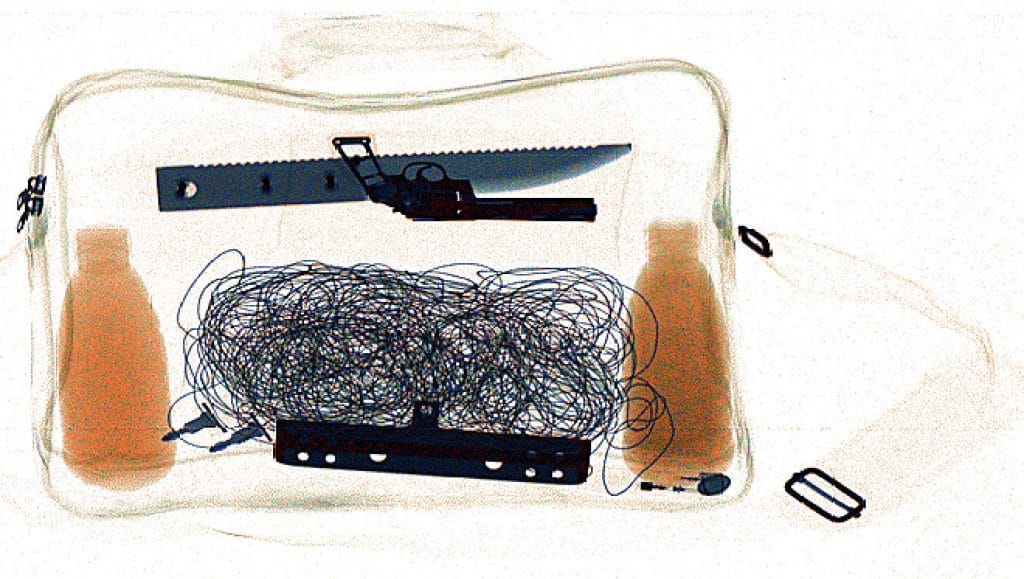
The X-Ray Baggage Scanner is the most commonly used system for scanning baggage at entry points. Whether you are entering a secured building while carrying luggage or your bag or at the airport, you will be required to leave your luggage on the machine with a conveyor belt for security scanning.
With this x-ray baggage scanner, the operator can see the imaging, which shows what the bag contains and can identify potentially dangerous or smuggled objects before one is allowed into the building or the airport.
The X-ray baggage scanner uses a small measure of x-rays to illuminate the objections under inspection, uses a computer to analyze the rays transmitted, and then analyze the behavior of the penetrated objects according to the changes in the transmitted rays.
Typically, the display screen’s image is computer-generated and highlights objects of dangerous nature based on the color changes. While the x-ray baggage scanner does not affect digital products, it has harmful effects on the human body. Fortunately, this scanner’s body and lead curtain minimize the leakage of x-rays.
X-Ray Backscatter Used in Security Checking
To keep the airport safe and protect travelers, airports employ different scanning equipment to check unauthorized carry-on objects and scan luggage for these items. Such screen equipment includes metal detectors, backscatter x-ray machines, and millimeter-wave machines.
The backscatter x-ray machine uses ionizing radiation to identify objects hidden by passengers and present graphical images of the luggage. By identifying these objects, the backscatter scanners can detect security threats from explosives or weapons that a passenger could be hiding under their clothes.
The beauty with the backscatter x-ray machine uses low x-ray energy, which is not harmful to anyone’s health. By design, it performs full-body scans, allowing it to operate even if one side of the target is exposed to the examination.
Conclusion
The role of x-rays in security inspection can’t be understated. As the challenges posed by insecurity grow, so is the demand for a tight security check. X-ray security scanners have been designed to offer safe, non-contact scanning for people and their luggage to ensure that dangerous and unauthorized objects don’t find their way to the buildings, airports, ships, and railway stations.
The X-ray baggage scanners and backscatter x-ray scanners are useful x-ray inspection machines employed to identify threats from weapons, explosives, and drugs. Once the threat is identified, laid down security procedures are followed to minimize the occurrence of security incidents that can lead to loss of life.
Featured image source: Uni X-ray Technology