If you are into sports, you must know how no of two matches are the same. However, there are similar methodologies and strategies regularly utilized by sportsmen who have been proven to be effective time and again. Likewise, when a hacker is attempting to breach a system, he will not re-invented a strategy except if he really needs to. An attacker uses basic kinds of hacking techniques which have been proven to be the most effective; for example, phishing, malware, cross-site scripting (XSS) and DOS. Following are the most widely recognized network attacks seen today.
1. Reusing Credentials

Nowadays users have such a large number of passwords and logins to recall that it’s enticing to reuse the same information anywhere to make life somewhat less demanding. Even though security best practices all around prescribe you to have different passwords for every one of your applications and sites, numerous individuals still reuse the same passwords which are what attackers rely on. Regardless of how convenient it might be to reuse the same password everywhere, one day when any of your profiles are hacked, then the hacker will get easy access to all the other data such as your email, social media handles, online bank account, etc. The best way to stay safe from credential theft is by changing and updating your login data on a regular basis. You should also create complex and long passwords which are hard to crack. Try using an online password generator and avail different web security coupons to enhance your online safety.
2. Phishing
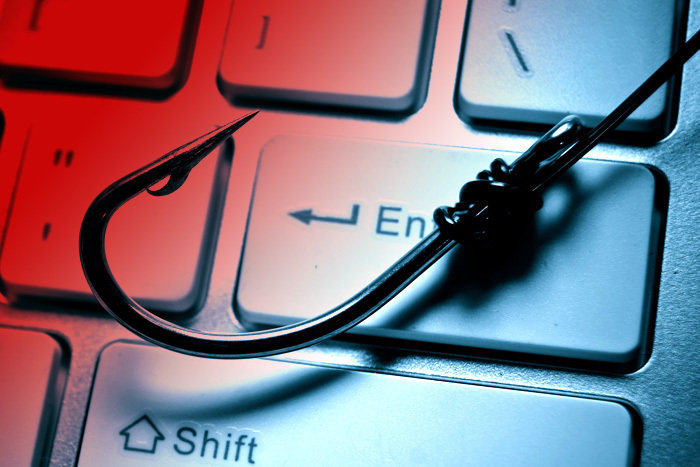

In this type of network security attack, you may receive an email that has all the earmarks of being from somebody you trust or know such as your manager or a friend. The email will appear to be real and alert you about something (for example an unrecognized login attempt on Facebook). In such emails, there is always a link to click or an attached file to open. Once you click the link or open the corrupt file, you will introduce a virus or malicious malware in your device. Sometimes after clicking the link address, you might be sent to a real looking site that requests you to sign in to respond to a critical request however that is a cover up used to catch your login details when you attempt to sign in. To protect yourself from phishing attacks, verify your contacts, email senders and scan received files and attachments with antivirus.
3. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
In a SQL infusion attack, a hacker attacks a weak site to steal its confidential and stored information, for example, sensitive monetary information or client credentials. A standout amongst the most popular ways an attacker can send an XSS is by sending a malicious code into a comment that would run automatically. For instance, they could insert a link to a corrupt JavaScript in a comment on any website or blog. XSS attacks can harm the reputation of a site by putting the clients’ data in danger. Any delicate data a client sends to the webpage, for example, their passwords, MasterCard data or other sensitive information, can be stolen through XSS without users suspecting any maltreatment. To put a stop to cross-site scripting attacks is to disinfect user input. Sanitizing data is a strong security, but should not be used alone to encounter XSS attacks. Sanitizing user input is in particular helpful on sites that allow HTML markup, to guarantee data received cannot harm the users over and above your database by scrubbing the data clean of potentially harmful markup, altering unacceptable user input to an acceptable format.
4. Brute Force Attacks

Brute Force attacks are used to crack the entrance of a network. As opposed to making a client to download malware, the attacker attempts to find the code or password to break into the network or system by trying different passwords through experimentation. Trying one password after another can be tedious, so hackers ordinarily use automatic password generating programs or software to enter several passwords. Long and complex passwords are comparatively harder to find than the basic ones such as, “qwerty,” “123456789” or your date of birth.
Conclusion:
There are many ways to breach, corrupt or destroy an online system. Hackers are coming up with new ideas now and then. We can keep our online presence safe and secure by putting in a little time and effort. Follow the safety guards mentioned above, and you will be able to protect your devices against the common types of network attacks.
You’ll also like to read: Protection From Common Network Attacks (Part 1)