Nowadays, Android phones are used by most people in the world. Unlike iPhone, Android phone’s storage can be extended by adding SD card. The inner memory of a smartphone is limited and small, if we can create a second ext2/ext3 partition from SD/TF card as inner memory, that would be great! So how to partition SD card? Here, we highly recommend you try AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard.
Functions of AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard
AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard is a free partition software for Windows. Although AOMEI Partition Assistant has many editions. For common users and this task, its Standard Edition is enough to use.
First, I’d like to introduce you some useful features of AOMEI Partition Assistant: resize/move partition, merge partitions, copy disk/partition, migrate OS to SSD, create/format/delete partition, split partition, extend partition wizard, partition recovery wizard, make bootable CD wizard, Windows to Go creator, quick partition, command line partitioning, etc.
How to Partition SD Card Using AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard
To use AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard to partition SD Card/TF Card is very easy. Install and run AOMEI Partition Assistant. Connect your SD or TF card to computer via a card reader. If you plan to direct connect your SD card to computer via phone, please make sure break the USB connect.
Create the second ext2/ext3 partition on SD card has two parts. Part I is shrinking the original partition to make an unallocated space.
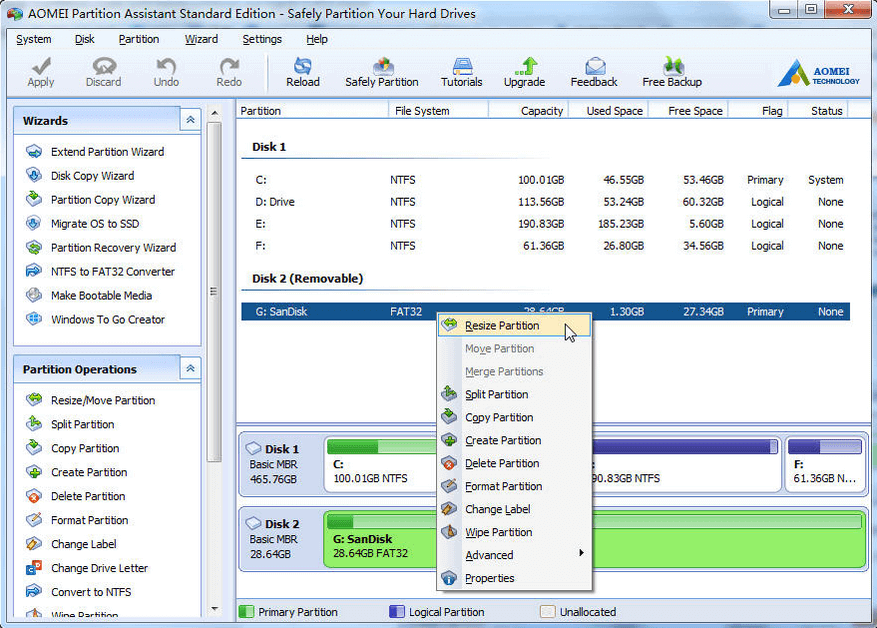
Part II is creating partition on the unallocated space.
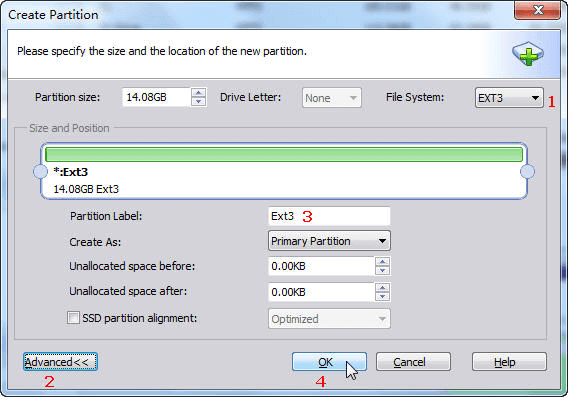
For more details on how to partition SD card for Android with free SD card partition tool ‘AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard’ please visit here.
AOMEI Partition Assistant is very useful and safe to use free partition software. Not only partition SD Card/TF Card, but also partition your hard drives and USB flash drive. It is a necessary tool to optimize your disk and system. Thanks AOMEI Technology to make our life easier.
ext2 or second extended file system is still the file system of choice for flash-based storage media (such as SD cards and USB flash drives) because its lack of a journal increases performance and minimizes the number of writes, and flash devices have a limited number of write cycles.