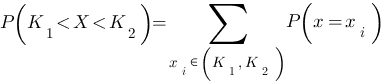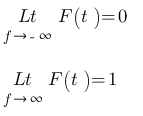Binomial Distribution
This is also a random variable distribution. A random experiment is conducted n times independently. Suppose E is one event of the experiment, P is its probability. If each time the event occurs treat it as success otherwise treat it as failure then probability for success is equal to P.
Probability for failure (say) q = 1-p → p+q =1.
Now, out of the ‘n’ times number of success that we may get it 0 or 1 or 2 or…………..n
Probability of getting r times success =
The random variable distribution in the values of random variable are the number of success is called Binomial Distribution.
Now, the binomial distribution can be written as follow:
Probability Distribution Function
Symbol :-
If x1, x2, x3,…….., xn are values of a random variable X, then
for any two real number K1, K2.
for any real number K.
Definition :-
Probability distribution function of a random variable X is denoted by F and is defined on R as follow:
Properties :-
If F is an imaginary function, then
Theorems :-
- The arithmetic mean of binomial variable X with parameters n, p is the product of n and p ie., n.p | here n is the number of times that the experiment is conducted and p is the probability of success.
- Variance of a binomial variable X with parameters n, p is n.p.q where q = 1 – p